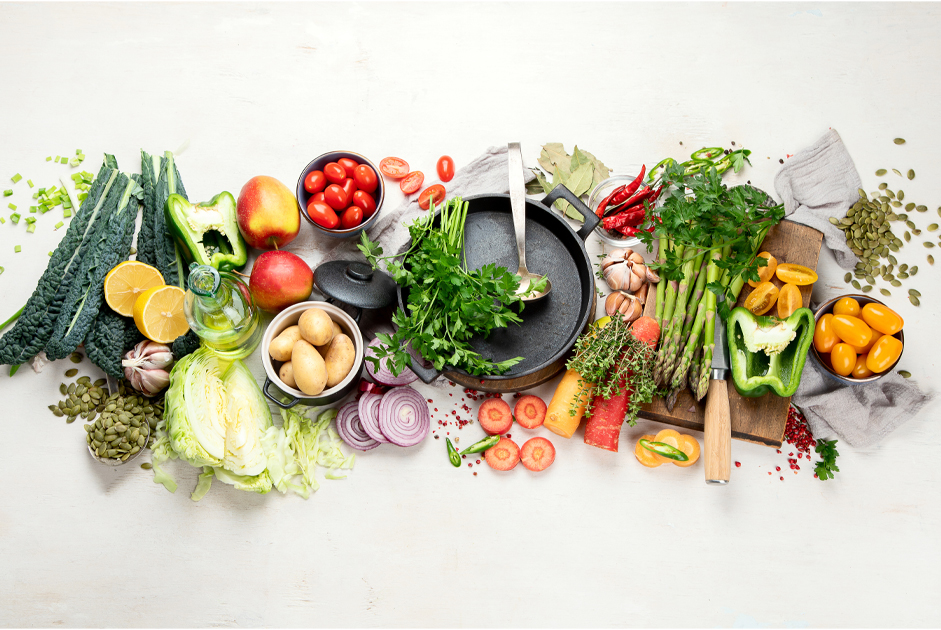
Plant based eating has gained significant popularity, with various diets emphasizing different levels of plant consumption. Among the most popular are plant forward, vegetarian and vegan diets. While these diets share a common focus on plant foods, they differ significantly in their guidelines and restrictions. Understanding these differences can help you make informed choices about your dietary preferences and nutritional needs.
Plant-Forward Diet
Are you curious about consuming a more plant-based diet but do not want to cut out animal foods completely? A plant-forward diet is a diet that emphasizes vegetables, fruits, grains and legumes but does not necessarily eliminate animal based foods. Meat or other animal based foods may be included in a meal but are usually not the main component.
Vegetarian Diet
A vegetarian diet is a way of eating that focuses on plant based foods while excluding meat, poultry and fish. This diet includes various fruits, vegetables, legumes, nuts, seeds and grains, providing a rich array of nutrients essential for good health. There are several types of vegetarian diets that have additional allowances and/or restrictions. Some vegetarians may also include dairy products and eggs. A vegetarian diet can be both nutritious and delicious by emphasizing whole, unprocessed foods, supporting overall well being and environmental sustainability.
Vegan Diet
A vegan diet is a type of plant based diet that excludes all animal products. This means no meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs or any other animal derived ingredients. Vegans also steer clear of products that involve the use of animals, such as honey and specific food additives. A well planned vegan diet can provide all the essential nutrients the body needs. However, attention must be given to certain nutrients like vitamin B12, iron, calcium, omega-3 fatty acids and protein which are more commonly found in animal products.
Benefits of These Diets
By following one of these diets, you may benefit from a decrease in the risk of heart disease, stroke, obesity, high blood pressure and cholesterol, type 2 diabetes and many cancers. Some meats are high in saturated fat which can lead to poor heart health. Processed meats like deli meat, bacon and sausage are usually high in sodium and can increase blood pressure. A well balanced vegan, vegetarian or plant forward diet can offer numerous health benefits, including a lower risk of chronic diseases, better weight management and improved digestion. By emphasizing whole, unprocessed foods, these diets can be both nutritious and delicious, supporting overall well being and environmental sustainability.
As interest in plant based eating continues to grow, understanding the differences between plant forward, vegetarian and vegan diets is crucial for making informed dietary choices. Each of these diets offers unique benefits and allows for varying degrees of animal product consumption. Whether you choose to adopt a plant forward approach, embrace vegetarianism or commit to a vegan lifestyle, focusing on plant based foods can lead to numerous health benefits, as mentioned earlier.
Remember, the key to a successful transition to any of these diets is to emphasize whole, unprocessed foods and ensure you are getting a balanced intake of essential nutrients. By making mindful and informed choices, you can enjoy a diet that is not only nutritious and delicious but also supports your health and the environment.